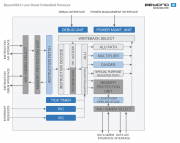
-
IP

-
ProcessorsGeon Secure Execution ProcessorSecurityBA20 PipelineZero Embedded ProcessorBA21 Low-Power Embedded ProcessorBA22-DE Deeply Embedded ProcessorBA22-CE Cache Enabled ProcessorBA22-AP Basic Application ProcessorBA25 Advanced Application ProcessorPeripheralsAC97 Audio ControllerSubsystemsDDR2/DDR SDRAM Memory ControllerGeneral Purpose Debug Interface ControllerGPIO ControllerJTAG TAP (Test Access Port) ControllerMAC 10/100/1000 Ethernet ControllerSDRAM/FLASH/SRAM Memory ControllerPCI 32 Bridge ControllerUART 16550 Serial ControllerVGA/LCD Display ControllerEvaluation
-
-
Processors

-
Security

-
Peripherals

-
Development tools

-
Corporate

Beyond BA21 Low-Power Embedded Processor
Designed for deeply-embedded systems or as an auxiliary processor in larger systems, Beyond BA21 Low-Power Embedded Processor (BA21) delivers better performance than most processors of its size while having particularly low power requirements. It is an effective choice for wireless communication, analog peripherals management, or other mixed-signal functions in energy- and cost-sensitive applications.
Binary-compatible with other members of the silicon proven BA2x family of processor cores, BA21 implements relatively simple and extremely compact instruction set, providing the highest code density in its class, without compromises on performance, ease of use, or scalability.
|
High Performance 32-bit CPU
|
|
|
Processing Efficiency
|
|
| Fast & Flexible Memory Access |
|
|
Optional Processor Units
|
|
| Available Pre-Integrated Platforms |
|
| Easy Software Development |
|
 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) together with processor architecture defines a software view of processor family as seen by programmer. It has prevailing impact on several key processor characteristics, including code density and ease of software development.
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) together with processor architecture defines a software view of processor family as seen by programmer. It has prevailing impact on several key processor characteristics, including code density and ease of software development.The BA2x ISA was designed from ground up with design goal achieving highest code density among 32-bit processors with no compromise on performance. To achieve such ambitious goal it was necessary to rethink how ISA is designed. Often instruction set is defined with legacy constraints and by processor architects who are coming from hardware background. We have instead dropped all legacy constraints and first developed a fully working and optimized compiler for initial ISA proposal. This allowed us to do conclusive benchmarking on vast code base, comparing results with other architectures and finding new, better solutions.
Ultimately, ISA design is an optimization problem. Iterating through numerous approaches, ideas, optimizations and also dead ends we finally settled on BA2x ISA that is (based on our benchmarks) best fulfilling our design goal of highest code density at no compromise on performance.
The resulting BA2x ISA has 32 general purpose registers, all addressable with all register operand instructions. It also features cleverly encoded 16-bit, 24-bit, 32-bit and 48-bit instructions for maximum code density with simple decoding.
The smaller the processor, the more ISA matters. Best example of BA2x ISA is Beyond BA20 PipelineZero processor, capable of outstanding performance per MHz at extremely small area and ultra-low power consumption.
|
Code density
Reducing ASIC power and cost
|
|
| Ease-of-use |
|
|
Performance
32 GPRs, small static instruction count
|
|
| Extensibility |
|
To facilitate the software development and testing as well as ensure code compactness and stability, Beyond provides customers with a comprehensive range of development tools:
BeyondStudio Integrated Development Environment
Major components of BeyondStudio
| Eclipse based IDE with all of its generic functionalities |
|
||
| Integrated GNU based cross compiling toolchain |
|
||
| Supported library |
|
||
| Instruction set simulator (basim) |
|
||
| Custom tools and plug-in components allowing for easy deployement of binary to simulator or hardware targets. | |||
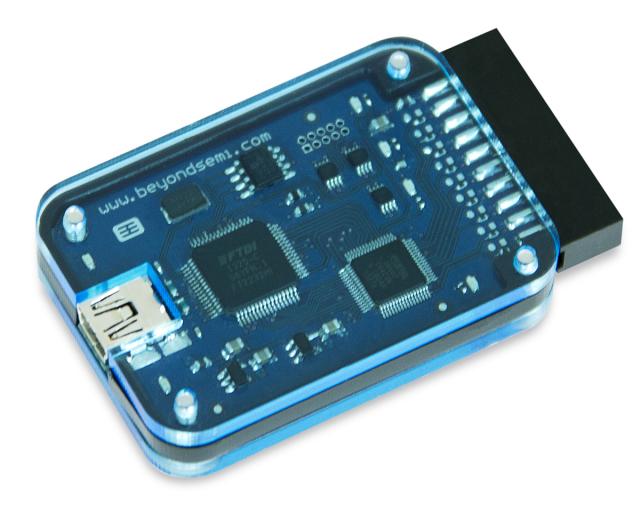
Beyond Debug Key
|
Beyond Debug Key is an essential tool for embedded software development, enabling access to processor debug features through JTAG interface and simultaneous connection to UART serial console.
Featuring USB 2.0 connection to PC and wide target IO voltage range it is a compact debug and diagnostics tool. Beyond Debug Hub is fully compatible with Beyond BA2xTM processor family as well as majority of other processors.
In addition to IEEE 1149.1 and IEEE 1149.7 standard JTAG signal set it also supports proprietary One Wire Debug and Two Wire Debug protocols. With appropriate software it can be used to perform various IC level and board level diagnostics.
|
|
Linux and Android Development Tools
| GNU based cross compiling toolchain |
|
| Supported libraries |
|
If you would like to inform yourself further about Beyond Semiconductor products, please complete the webform below and let us know your questions, requirements or requests.
Please note that all submitted information will be handled confidentially and used only to address your inquiry. Therefore, we kindly ask you to fill out all the fields of the form.
You may expect our answer shortly.
Copyright © 2006 - 2024 Beyond Semiconductor. All rights reserved.